How a water softener works
 Ion exchange involves the use of a resin bed. Ion exchange resin is a very small synthetic bead-like material that looks a little bit like brown sugar. The beads are very small, about the size of a pin head.
Ion exchange involves the use of a resin bed. Ion exchange resin is a very small synthetic bead-like material that looks a little bit like brown sugar. The beads are very small, about the size of a pin head.The process is called Ion exchange because the ions calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) are exchanged for small amounts of sodium (Na).
Hard Water
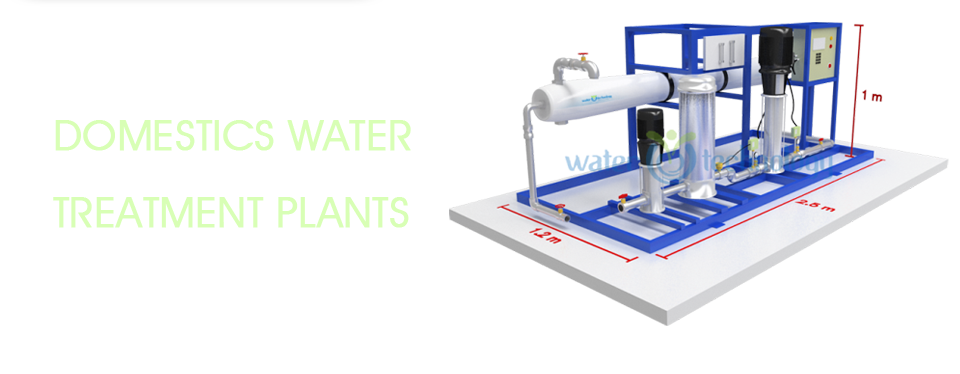
 Here a drop of hard water containing magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) approaches the resin.
Here a drop of hard water containing magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) approaches the resin. Here a drop of hard water containing magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) approaches the resin.
Here a drop of hard water containing magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) approaches the resin.
 As the drop of water passes through, the resin prefers magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) to sodium (Na) so they swap.
As the drop of water passes through, the resin prefers magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) to sodium (Na) so they swap.
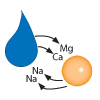
 The resin now has magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca)…
The resin now has magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca)…
Soft Water
 …and the soft water contains a small amount of sodium (Na).
…and the soft water contains a small amount of sodium (Na).
Water Softening Methods
Water softening is a process that reduces calcium, magnesium and ion concentration in hard water. Hard water is known to clog pipes and to complicate soap and detergent dissolving in water. Temporary hard water contains Calcium and Magnesium Bicarbonates. While permanent hard water contains Calcium and Magnesium Chlorides and Sulphates. The temporary hardness can be removed by boiling the water and then filtering it. The permanent hardness can be removed by addition of washing soda. The best way to soften water is to use a water softener unit and connect it directly to the water supply.Determining the hardness of the water is important before attempting to soften it. A high mineral content will cause problems like scaling of hot water geysers, choking of pipes, poor quality of washing in machines etc. There are several methods of softening hard water. Following are important water softening methods.
Ion exchange water softener:
This method is suitable for all appliances which uses a lot of water. This method can also increase the life span of dishes and clothes. Ion exchange water softener depends on two tanks- the brine and resin tanks. Potentially hard water will pass through the resin beads in resin tank. When the beads become saturated with magnesium and calcium ions, the ion exchange softener goes offline. Brine tank is again filled with new sodium ions which are ready for exchange, it flushes the resin tank and then it becomes online again.Shower head water filters:
The shower water filters use the most effective methods to catch lead, chlorine, unpleasant smell from the water your shower in. The KDF (Kinetic Degradation Fluxion) water filtration technology is used in shower water filters. The KDF redox process works by exchanging electrons with contaminants. This "give and take" of electrons converts many contaminants into harmless components. During this reaction, electrons are transferred between molecules, and new compounds are created. Some harmful contaminants are changed into harmless components. KDF frequently found in home showerhead filters because of its effectiveness at higher operating temperatures and flow rates.Reverse Osmosis (RO):
Reverse Osmosis is active at a comparably low temperature and its energy consumption is rather economic, people use it with different applications, for example, cleansing of polluted water, desalination, minerals' reclamation, regulating percent of whey and various food products and water filtration. Most RO devices with a cellulose acetate membrane are worked out to act between 55 F – 86 F (13 C – 30 C). Actually, the dirty water can pass through one of or a set of the following points: chlorinator and retention volume, anthracite filter, degasifier, neutralizer, sand bed, activated charcoal filter, microfilter, and deionizer, it depends on the kind of filtered water and the quality of water you want to receive after filtration.Water filter pitchers:
Using water filter pitchers is the best choice for home water purification which is needed more in today's world. Most water filters can remove phthalate contamination and cryptosporidium from drinking water but water filter pitchers can remove a broader range of contaminants and at a significantly higher level of viruses, bacteria, chlorine, metals, and are BPA free. This is the cheapest and safest way to purify drinking water.Water softening by magnetic:
Magnetic water softeners employ magnets placed either inside or outside a water pipe so that water flows through a magnetic field. Because of the strength of the magnetic field, water is stripped of its impurities and "hardness," but not of vitamins and nutrients. It is best to put magnets as close to the water source as possible. It is considered to be the safest for drinking water on the market and one of the few non-chemical ways of softening water.Chemical method:
Chemical method is the most inexpensive way of treating hard water. Two chemicals used in the water treatment are sal soda and Calgon.Salt:
The water that enters the house is filtered through the zeolite minerals. A reaction occurs during the treatment process which replaces the magnesium and calcium ions to be replaced by sodium. The minerals containing zeolite require change on a periodic basis. This system includes a large tank where the bags of softener salts are regularly added.
Calculation example:
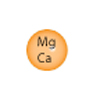
5 people in home, 10 grains per gallon hardness.
- 1. 5 people X 70 gpd = 350 total gpd
- 2. 350 gpd X 10 grains = 3500 grains per day
- 0.75 cubic ft. @ 19,000 grains / 3500 = 5.4 days between regenerations
- 1.0 cubic ft. @ 25,000 grains / 3500 = 7.1 days between regenerations
- 1.5 cubic ft. @ 38,000 grains / 3500 = 10.8 days between regenerations
- 2.0 cubic ft. @ 50,000 grains / 3500 = 14.3 days between regenerations
The best choice would be the 1 cubic foot unit (closest to 7 days).

Water Softener Capacity Calculation
Ideally, a water softener should be sized so that it does not regenerate any more often that every three days (wastes water and salt), nor go longer than 14 days before regenerating (can cause compacting of resin, and fouling with sediment or iron). 7 days between regenerations is probably best - especially if iron is present. For the majority of homes, our 1 cubic foot unit is more than enough capacity. There are conditions that would create a need for a larger unit: larger family (6 or more) and/or very hard water (over 15 grains). Use the following formula to calculate the proper size:
- Multiply the number of people in your family times 70 (gallons of water used per day, national average).
- Multiply the answer by your water hardness in grains per gallon (to convert mg/l or ppm to grains, divide by 17.1). If iron is present, add 5 grains for every ppm (mg/l) of iron (iron MUST be dissolved iron - it appears clear from the tap but leaves reddish-brown stains).
- This is your "grains per day" number. Divide this number into each of the softener capacities until you find the best size.
Note:
With the Autotrol Logix computer-control valve, you can choose between three settings:- "S" Standard Salt Usage Setting (most widely recommended)
- "L" - Low Salt Usage Setting
- "H" - High Salt Usage Setting
How ion-exchange water softeners work
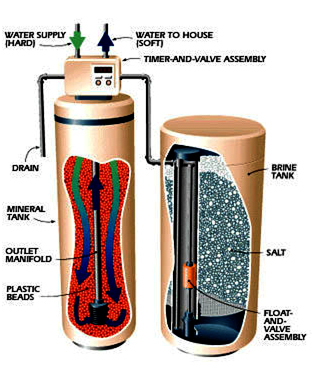
Conventional water softeners have two separate chambers, the resin tank and the brine tank, and use an ion-exchange process to remove the hardness ions calcium and magnesium. Softeners often are able to remove not only calcium and magnesium, but also iron, manganese and radium. Raw feed water is passed through a bed of resin "beads" inside the resin tank where the hardness ions in the feed water trade places on the resin beads with sodium ions that are electrostatically bound to the beads. Eventually, the resin exhausts its supply of sodium and must be "regenerated." When the beads have no more room for additional calcium and magnesium ions, the unit temporarily goes off-line and the resin tank is flushed with salt water from the brine tank, the source of new exchangeable sodium ions.
Thus, the product water produced by softeners will have no calcium and magnesium, but additional sodium, about 8 mg/L per grain of hardness. Routinely, water softeners are plumbed so that the feed water destined for drinking bypasses the softener when consumers have been placed on low-sodium diets.
The regeneration process involves draining from the resin tank the saltwater solution, now with the added calcium and magnesium ions, and discharging it.